12 Which of the Following Stimulates the Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex
Calcium released during muscle contraction stimulates PDH by increasing phosphatase activity for energy Production. Where does pyruvate dehydrogenase occur.
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex Biochemistry Animations Mechanism Regulation And Inhibitors Youtube
Which of the following is true of the regulation of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex.
. Lipoamide dithiol is reoxidized by a cystine of E3 E2E3 to give two cysteine residues 4. In the presence of high energy signals ATP NADH the PDH is turned off. Why does acetyl CoA a product of fatty acid catabolism influence the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex PDH a control point in carbohydrate catabolism.
Insulin stimulates all of the. Pyruvate is then transported into mitochondria and converted to acetyl-CoA by the pyruvate-dehydrogenase complex. First week only 499.
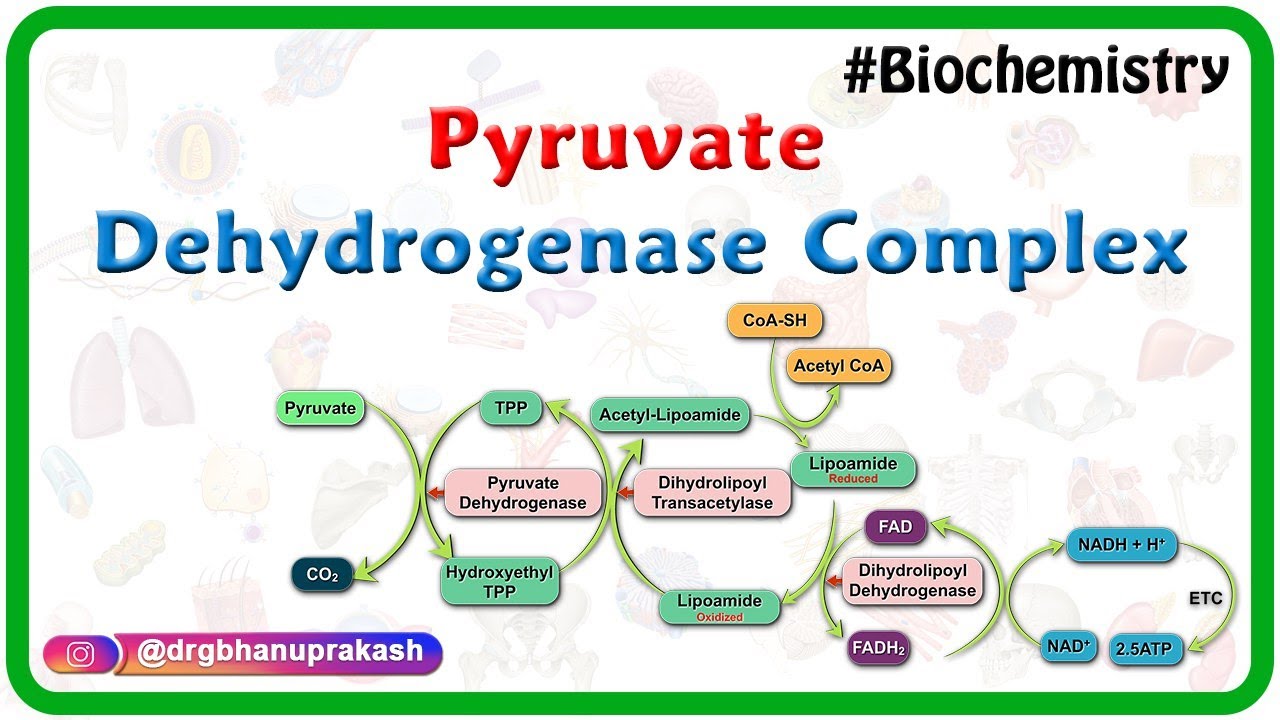
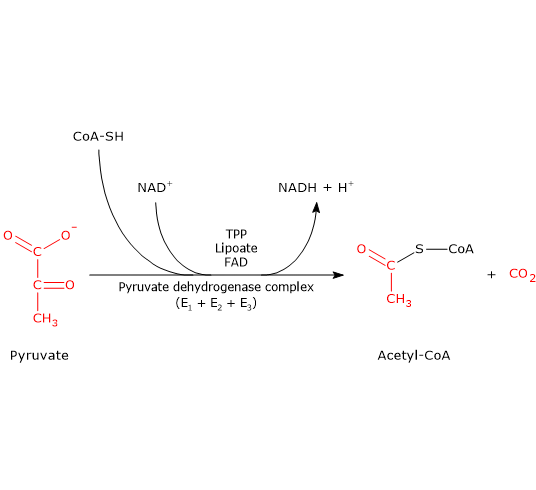
The coenzymes of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex PDC is a complex of three enzymes that converts pyruvate into acetyl-CoA by a process called pyruvate decarboxylation. 101 In the resting.
NADH is a key inhibitor of the activity of α ketoglutarate dehydrogenase see figure 2012. 1 When fatty acid breakdown is inhibited ADP is low causing a decrease in activity. 11 of the following is a product of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex.
Give one metabolic intermediate that is released as pyruvate is oxidizes by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. The goal of the treatment for pyruvate dehydrogenase complex PDC deficiency is to stimulate the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex to produce as much energy as possible. Question is Which of the following enzyme does not take part in the TCA cycle Options are A Citrate synthase B Iso-citrate dehydrogenase C Pyruvate dehydrogenase D Malate dehydrogenase E Leave your comments or Download question paper.
Insulin indirectly stimulates glucose oxidation via increasing glucose uptake and subsequent glycolysis that increases pyruvate supply for mitochondrial glucose oxidation by the pyruvate dehydrogenase PDH complex the rate-limiting enzyme of glucose oxidation. Pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency is a rare neurodegenerative disorders associated with abnormal mitochondrial metabolism. Start your trial now.
Acetyl-CoA may then be used in the citric acid cycle to carry out cellular respiration and this complex links the glycolysis metabolic pathway to the citric acid cyclePyruvate decarboxylation is also known as the pyruvate. The PDC is a multi-enzyme complex that plays a vital role as a key regulatory step in the central pathways of energy metabolism in. -when the cell is energy-depleted the kinase is inhibited and a calcium-dependent pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase is turned on-the phosphatase converts the PDH complex to the active dephosphorylated form-insulin is an activator of the PDH complex acting through the PDH phosphatase and promoting dephosphorylation.
It occurs in the mitochondrial matrix. This can prevent immediate worsening of the disease. Five coenzymes are used in the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex reactions.
ADP stimulates activity of the complex. Biology questions and answers. ADP stimulates activity of the complex 13.
The pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase will phosphorylate and inactivate the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Pyruvate dehydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyzes the reaction of pyruvate and a lipoamide to give the acetylated dihydrolipoamide and carbon dioxide. The E1 enzyme is dephosphorylated to inactivate it.
Acetyl-CoA then enters the tricarboxylic acid TCA cycle and electrons derived from it are donated to NAD and FAD leading to generation of intramitochondrial NADH and FADH 2. PDH kinase responsible to form inactive PDH is promoted by ATP NADH acetyl CoA while it is inhibited by NAD CoA pyruvate. The conversion requires the coenzyme thiamine pyrophosphate.
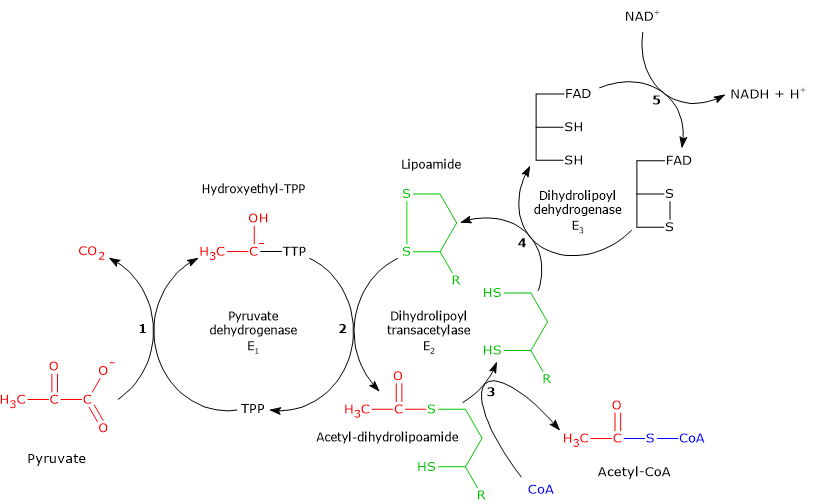
E2 of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex contains a lipoyl group that is covalently attached via an amide linkage to a residue on the enzyme a. Pyruvate reacts with TPP and is decarboxylated E1 Hydroxyethyl TPP reacts with lipoamide E1E2 2. Question 12 of 19 Select the factors that stimulate the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex dephosphorylation of E pyruvate dehydrogenase high ATP levels activating the regulatory kinase high concentration of NADH increase in Cat concentration high concentration of acetyl-CoA.
CO 12 of the following is true of the regulation of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. 2 When fatty acid breakdown is inhibited PDH is inhibited by acetyl CoA due to phosphatase activity. FAD regenerates the cystine to produce FADH2 E3 5.
Under these conditions might you expect to have a higher than normal blood concentration of which of the following metabolites. Thiamine pyrophosphate or TPP flavin adenine dinucleotide or FAD coenzyme A or CoA nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide or NAD and lipoic acid. A The E2 enzyme is phosphorylated to inactivate it.
A B -- C ΔG -1 C D -- E ΔG 3 E F -- G ΔG -5 The over. PDCD is a genetic disease resulting from mutations in one of the components of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. A deficiency in thiamine can reduce the activity of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex.
A series of reactions have the following ΔG. When the PDC is phosphorylated by pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase the PDC will become inactive. Type 2 diabetes T2D 5 is a growing public health issue in many countries It is generally accepted that carbohydrate oxidation is inhibited in the insulin-resistant heart and is concomitant with the development of outright diabetic cardiomyopathy The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex PDC connects glycolysis to the tricarboxylic acid TCA.
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is located in the mitochondrial. Treatment options typically include supplementing cofactors including carnitine thiamine and lipoic acid. Calcium ions play a role in the oxidation of pyruvate by activating the mitochondrial enzymes mediating the nonequilibrium and flux-generating reactions PDH complex citrate synthase NAD -linked isocitrate dehydrogenase and the 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex that supply the NADH and FADH 2 substrates for the mitochondrial complexes I and II.
Thiamine pyrophosphate is the active form of thiamine or vitamin B 1. Electrons stored in these two molecules are further. The lipoamide cofactor is reduced to inhibit the complex.
Lipoamide delivers an acetyl group to CoASH to produce Acetyl-CoA and lipoamide dithiol E2 3. 10 the cofactor to its pyruvate dehydrogenase enzyme component Premise Response FAD E TPP E Lipoamide E.

Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Comments
Post a Comment